Three laws of Newton are the fundamental laws which describe the motion of bodies. These laws are thus known as the Newton's laws of Motion. These laws help us to analyse the forces acting on a body and the effect of the forces on their motion. Let us discuss these laws and learn their importance and applications.
Newton's First Law:
When a body remains at rest it will tend to remain at rest until an external force is applied to it. Also, if a body remains in motion then it will tend to remain in motion until an external force is applied on it. Now lets understand it in a funny way, if you are sleeping in the morning then you will definitely want to sleep more until an external force like papa's words wake you up. Also, if you are playing in the lawn then you will always want to play more and more until same papa's words, which will be like and external force which makes you do something which you want to continue.
Jokes apart😀. Now considering scientific examples like when you are standing in a stationary bus, then which part of your body is in contact with the bus? your feet.. right??
so the feet will move along with the bus but the upper part of you body is still wanting to remain at rest and behave lazily and what happens? we tend to bend backwards. You must have had such an experience. And again looking at it with another aspect like suppose you are standing on the bus and the bus is moving with some velocity and when the driver suddenly applies brakes, then the part of your body which is in contact with the bus i.e. your feet, will come to rest instantly along with the bus but your upper body part it is still in jolly mood and want to remain in motion and as a result you fee a force towards front right? and you lean forward.
Now, let's work on more examples. Suppose, you are travelling by a train. And you are throwing any wrapper out of the window. ( But you shouldn't ) so now, what will happen? will the wrapper directly fall down following a vertical path?
No, the ball will still be in motion as it was before and thus it will not fall just downwards but it will also move some distance forward.
If you fall from an air balloon which is moving upwards with some velocity, then you will at first move a bit upward because of the inertia of motion and then when its velocity is zero, it will start falling downwards under gravity.
There are a lot more examples of the inertia of rest and motion.
Newton's second law of motion:
It states that the force applied on an object is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum and change in momentum takes place in the direction of force.
First of all let us learn what is momentum?
👉It is the product of a body's mass and it's velocity.
( p = mv ) where p denotes the momentum, m denotes the mass of the object or body and v denotes its velocity.
Now, what actually happens is suppose a body is moving with an initial velocity 'u'. Then, some amount of force is applied and under the action of force, the body accelerates.
Now, if the body will accelerate, its velocity will increase. The velocity will keep on increasing until the force ceases to act. Now, suppose that after acceleration, the velocity of the body becomes 'v' m/s.
Now, we can write that
initial momentum of the body = mu
final momentum of the body = mv
change in momentum = final momentum - initial momentum
rate of change of momentum = change in momentum / time = (mv - mu ) / t = ma
as a = ( v-u ) / t
So, we see that force can also be defined as the rate of change of momentum ( Here it is Linear momentum. There is also another term called angular momentum which we will be discussing further ).
And thus this explanation describes us the second law of motion.
Now, let's learn what is the law of conservation of momentum ?
The law states that the initial momentum of a system is equal to the final momentum of the system when there is no external force is acting on the system.
Now, the question arises that what is a system?
System is the area or space where our work is concentrated.
Suppose a ball '1' is colliding with another ball '2'. So, the system will be ball '1' and '2' together and we will be concentrating on their collision.
Now, let us consider that balls '1' and '2' are moving with initial velocities u1 and u2 respectively.
If u1 > u2, they will collide after travelling some distance. It means that if the ball '1' will be travelling with a greater velocity it will definitely collide with the ball '2' which is traveling with lesser velocity.
The bodies have collided and after collision they start moving with some different velocities suppose v1 and v2.
So, initial momentum of the system ( balls 1 and 2 ) is
m1u1 + m2 u2
final momentum of the system is
m1v1 + m2v2
So, from the law of conservation of momentum.
Initial momentum = final momentum
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
Newton's Third Law of Motion:
Newton's third law states that every action has equal and opposite reaction
Now, what does this mean?
This means that when you apply a force on any body or object you will experience the same amount of force.
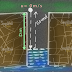
As you can see in the figure that the block's weight is applied on the ground and as a reaction force the ground applied a Normal force on the block. You can consider any example like hitting a wall with your hand the harder you hit the wall you also feel the same amount of force from the wall.
But one thing is very important here it is that both the forces are applied on two different bodies. If you think that both the action and reaction forces are applied on the block and cancel each other its wrong!!
In the figure you can see that the action force ( the block's weight) and the reaction force ( the normal applied by the ground) are being acted upon two different objects.
Now we can consider more examples on this. Do you know how rockets move?
The fuel burning there throws out the hot air from the rocket (you might have seen fire like thing at the bottom of it ) so as the hot air rushes outward from the rocket it pushes the rocket upwards as a reaction force.
When you jump on the ground from a height, you will experience pain on your foot. This happens because your feet applied some force on the ground as an action and the ground also applies the same amount of force on your feet so harder you fall harder you feel the pain
These are all examples of Newton's third law of motion.







Leave a Comment